up:: Content
author:: Rikke Friis Dam
full title:: 5 Stages in the Design Thinking Process
url: Link
Highlights
- methodology which provides a solution-based approach to solving problems (View Highlight)
- serves to understand the human needs involved, reframe the problem in human-centric ways, create numerous ideas in brainstorming sessions and adopt a hands-on approach to prototyping and testing (View Highlight)
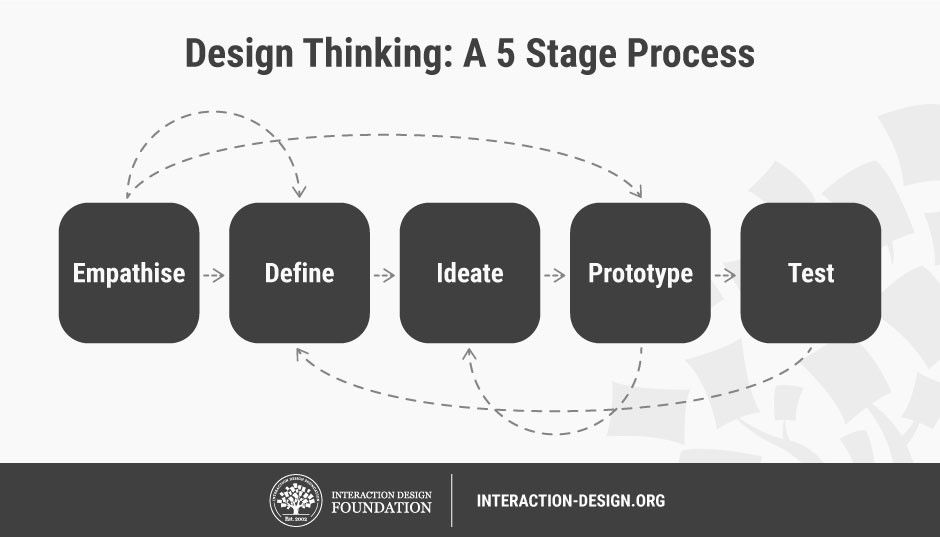
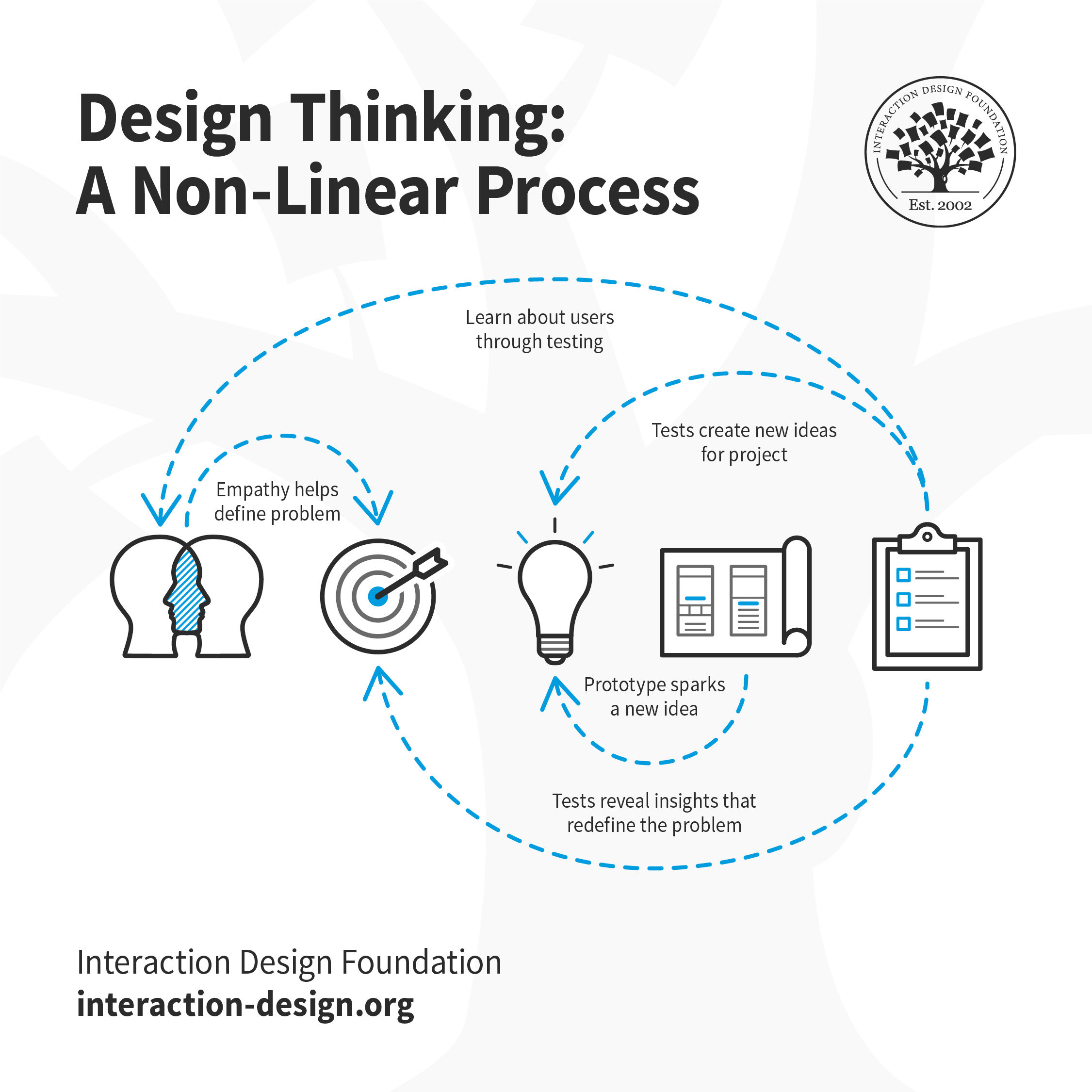
- non-linear, iterative proces (View Highlight)
- Stage 1: Empathize—Research Your Users’ Needs (View Highlight)
- Empathy is crucial to problem solving and a human-centered design process as it allows design thinkers to set aside their own assumptions about the world and gain real insight into users and their needs. (View Highlight)
- main aim of the Empathize stage is to develop the best possible understanding of your users, their needs and the problems that underlie the development of the product or service you want to create. (View Highlight)
- Define—State Your Users’ Needs and Problems (View Highlight)
- Defining the problem and problem statement must be done in a human-centered manner. (View Highlight)
- own wish or need of the company: “We need to increase our food-product market share among young teenage girls by 5%.” You should pitch the problem statement from your perception of the users’ needs: “Teenage girls need to eat nutritious food in order to thrive, be healthy and grow.” (View Highlight)
- Ideate—Challenge Assumptions and Create Ideas (View Highlight)
- look at the problem from different perspectives and ideate innovative solutions to your problem statement. (View Highlight)
- There are hundreds of ideation techniques you can use—such as Brainstorm, Brainwrite, Worst Possible Idea and SCAMPER. Brainstorm and Worst Possible Idea techniques are typically used at the start of the ideation stage to stimulate free thinking and expand the problem space. (View Highlight)
- Prototype—Start to Create Solutions (View Highlight)
- identify the best possible solution for each of the problems identified during the first three stages. The solutions are implemented within the prototypes and, one by one, they are investigated and then accepted, improved or rejected based on the users’ experiences. (View Highlight)
- Test—Try Your Solutions Out (View Highlight)
- igorously test the complete product using the best solutions identified in the Prototype stage. (View Highlight)
- The ultimate goal is to get as deep an understanding of the product and its users as possible (View Highlight)
 (View Highlight)
(View Highlight)- Knowledge acquired in the latter stages of the process can inform repeats of earlier stages. (View Highlight)